Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email already exists
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email does not exist
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent

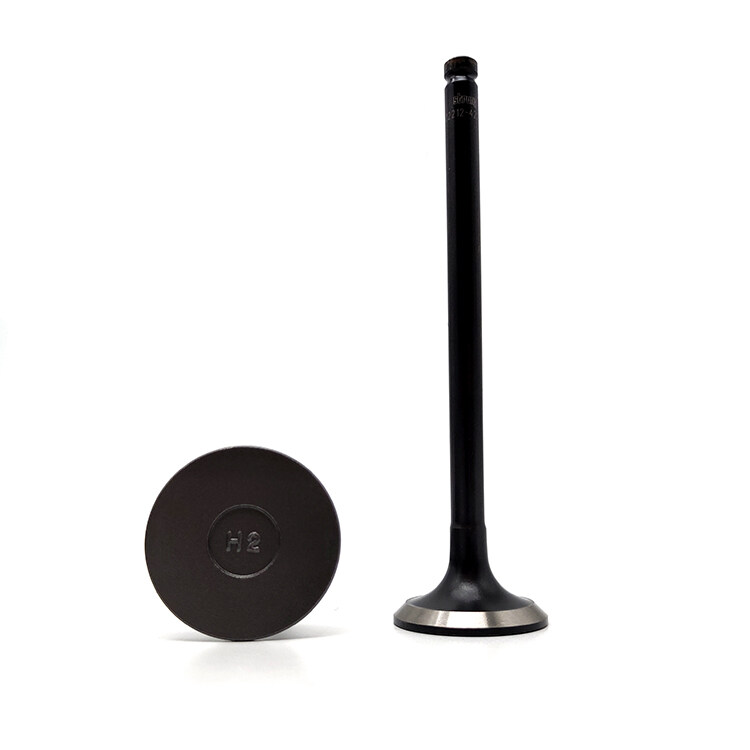
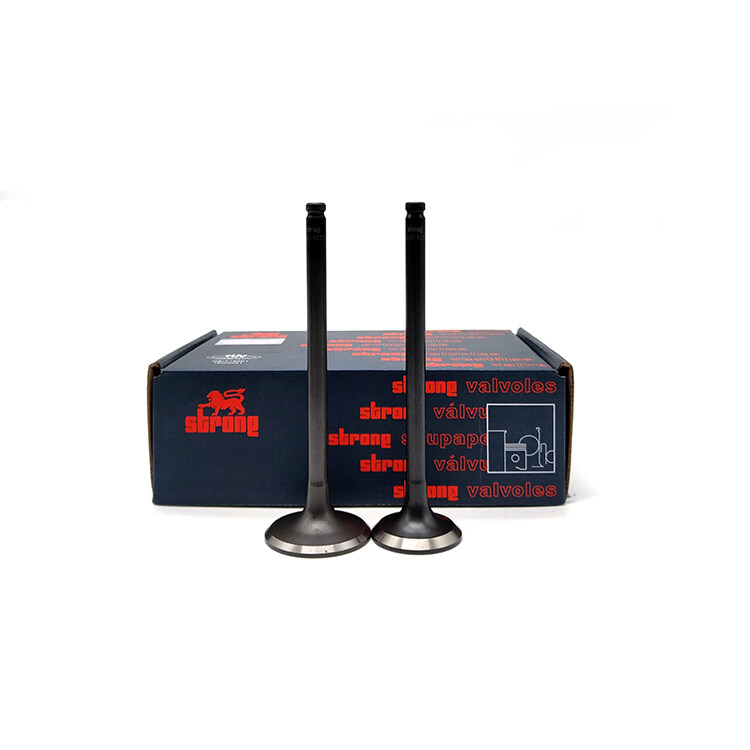
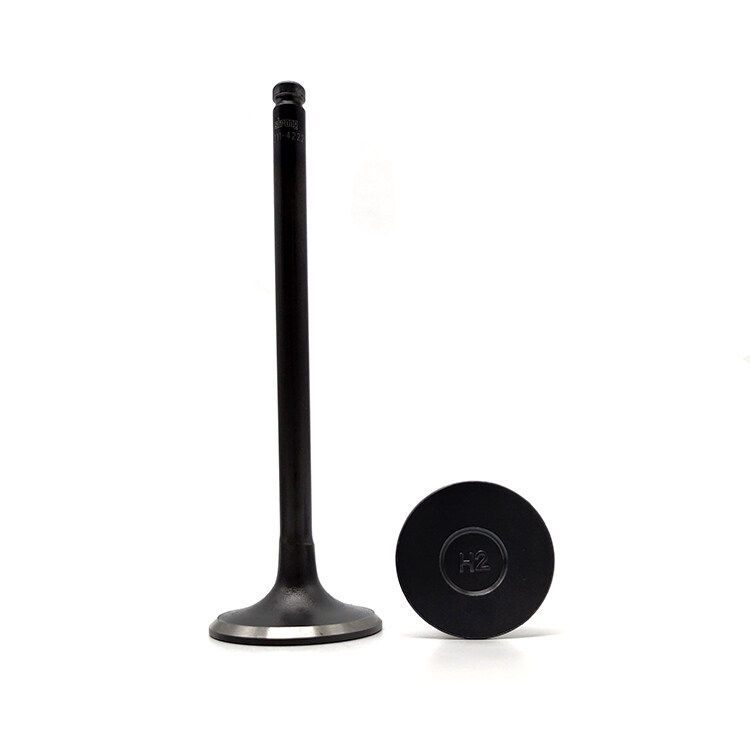
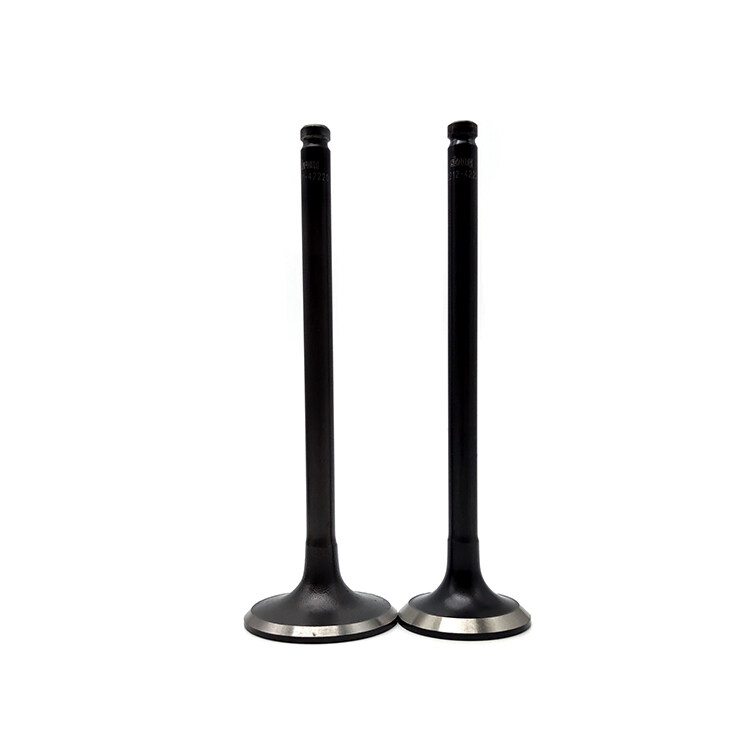
Wholesale Hyundai H100 Engine Valve
The Hyundai H100 is a light commercial vehicle, often used for various industrial and cargo transportation purposes. Its engine valves are a crucial component of its internal combustion engine, responsible for controlling the flow of air and exhaust gases in and out of the engine's cylinders.
The engine valves in the Hyundai H100 play a vital role in the overall performance and efficiency of the vehicle.
The Hyundai H100 typically features both intake valves and exhaust valves:
-
Intake Valves: Intake valves allow the entry of air into the engine's cylinders. Proper functioning of the intake valves is essential for ensuring the right air-to-fuel mixture for combustion. This impacts engine power and fuel efficiency.
-
Exhaust Valves: Exhaust valves open to expel the burnt exhaust gases from the cylinders after combustion. Their proper operation is critical for efficient engine performance and reducing emissions.
These valves are designed to open and close at specific times during the engine's four-stroke cycle, which is controlled by the camshaft. They are precision-engineered and made from durable materials to withstand the high temperatures and pressures associated with the combustion process.
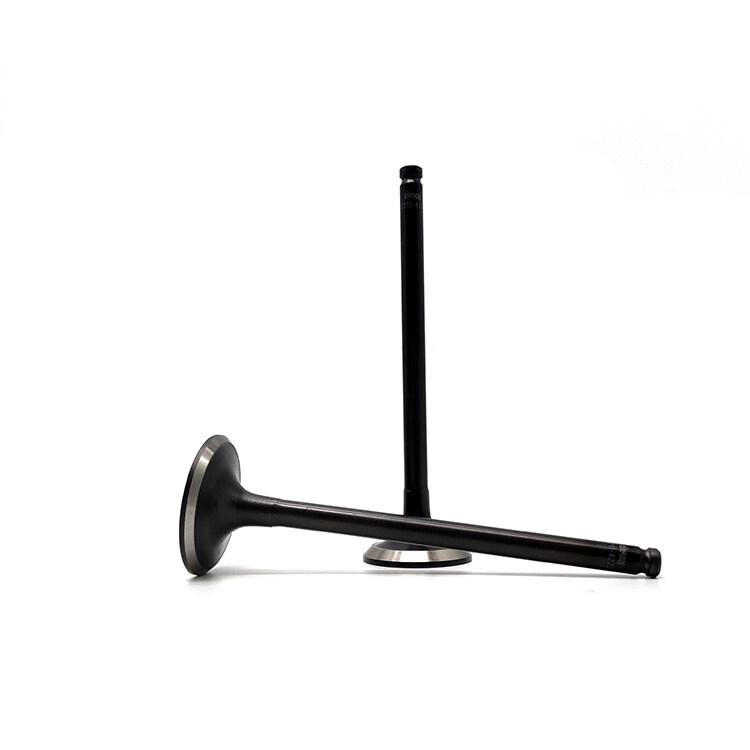
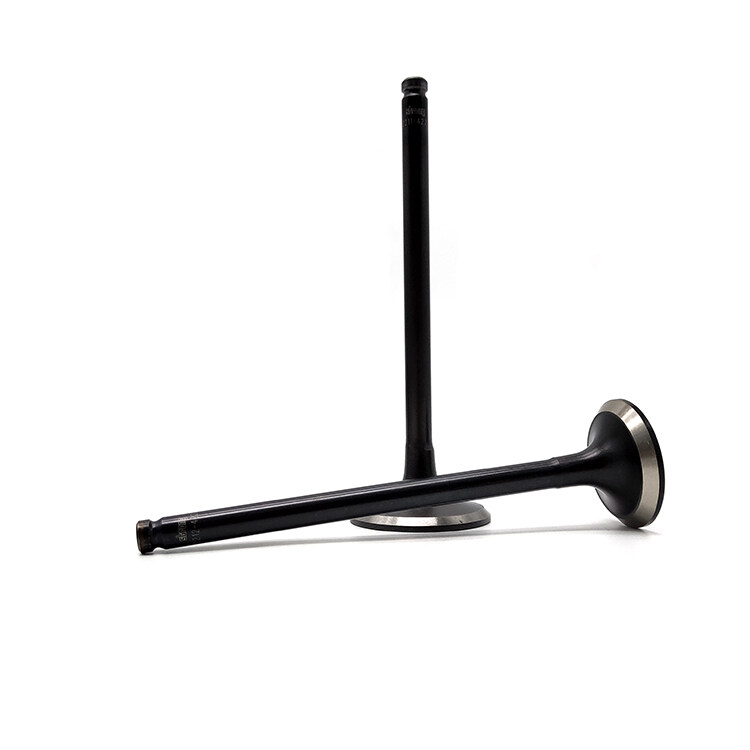
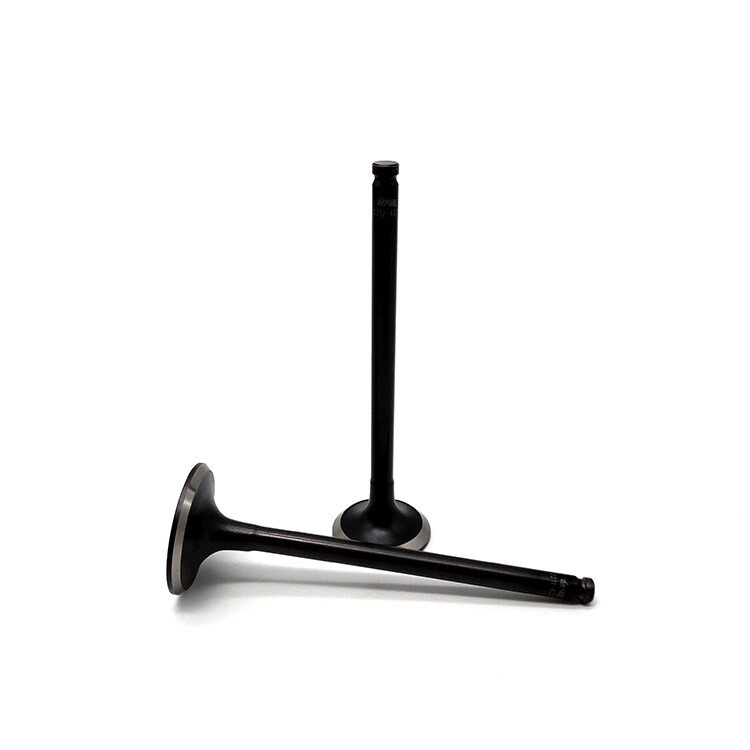
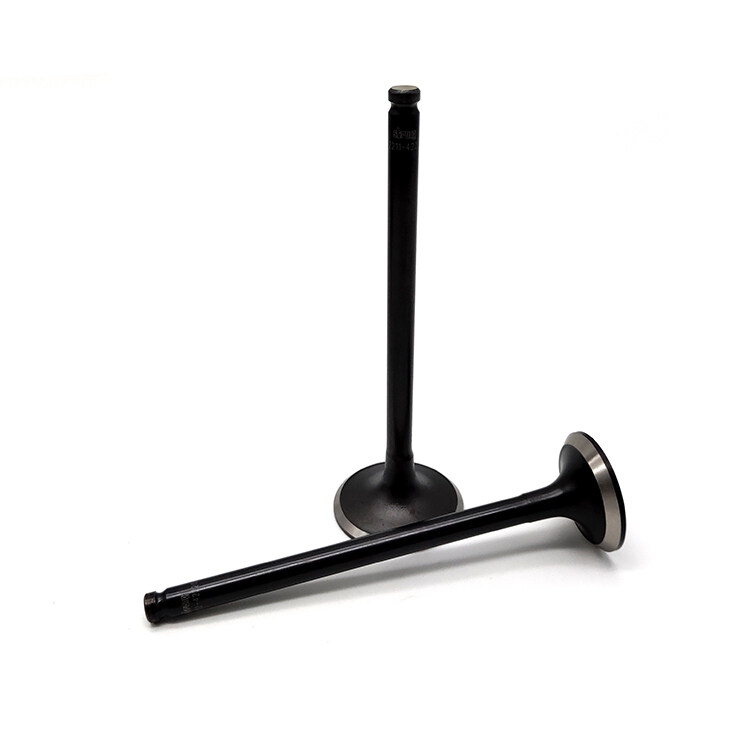
The engine valve features a tapered design that efficiently controls the flow of air in and out of the engine, allowing for precise timing of valve opening and closing. Made from high-strength materials, the valve is highly wear-resistant, ensuring long-lasting performance and reliability. Additionally, the valve is designed to withstand high temperatures and pressures, maintaining its stability and performance even under extreme conditions.
Help Engine Improve Efficiency:
According to the operating conditions of the engine, it can adjust the intake (exhaust) amount, valve opening and closing time, and angle very well to optimize the amount of incoming air and improve combustion efficiency. When the valve opens, it allows air and fuel to enter the engine’s combustion chamber, where it mixes and ignites to produce power. The valve then closes, trapping the air and fuel mixture in the combustion chamber, allowing it to burn efficiently. Once the combustion process is complete, the valve opens again, allowing the exhaust gases to exit the engine. By optimizing the valve’s timing and duration, the engine can achieve a more efficient combustion process, resulting in improved fuel economy and reduced emissions. Additionally, the valve’s design and material can also impact its efficiency.
Adjustable Design:
The valve requires adjustability to allow for tuning according to different operating conditions. As a result, the valve is typically designed to be adjustable. This adjustability allows for precise control of the valve’s opening and closing timing, which is essential for optimizing engine performance under different operating conditions. Adjustable valves are designed to allow for changes in the valve’s lift and duration, which can be adjusted to suit different engine speeds and loads. This adjustability is achieved through the use of adjustable valve lifters, which can be adjusted to change the valve’s lift and duration. The use of adjustable valves is essential in ensuring that the engine can operate efficiently and reliably under different operating conditions. By allowing for precise control of the valve’s opening and closing timing, the engine can optimize its performance, resulting in improved fuel economy, power output, and reduced emissions. Additionally, adjustable valves can help to reduce engine wear and tear, ensuring long-lasting performance and reliability.
Hyundai H100 Engine Valve Product Parameter:
|
Product Name |
Engine Valve |
|
Application |
Diesel Engine Parts |
|
Engine Number |
H100 |
|
Size |
STD |
|
OEM Number |
22212-42200 |
|
Condition |
100% Brand-new |
|
Size |
36.0*8.0*136.0mm |
|
Material |
21-4N |
|
Packing |
Neutral Packing |
|
Payment Way |
T/T, L/C, Paypal, Western Union, UPS |
|
Car Model |
Hyundai |
The role of the valve is specifically responsible for feeding air into the engine and discharging the exhaust gases after combustion. The engine structure, is divided into an intake valve (Intake valve) and an exhaust valve (Exhaust valve). The role of the intake valve is to suck air into the engine, and fuel mixing combustion; the role of the exhaust valve is the combustion of the exhaust gas and heat dissipation.

The role of the engine valve
The role of the valve is specifically responsible for the input of fuel into the engine and exhaust gas, the traditional engine has only one intake valve and one exhaust valve per cylinder, the design structure is relatively simple, low cost, easy maintenance, low-speed performance is good, the disadvantage is that it is difficult to improve the power, especially at high speeds when the inflation efficiency is low, weak performance.
To improve the intake and exhaust efficiency, now more than the use of multi-valve technology, common is each cylinder arrangement with four valves (there are also single-cylinder 3 or 5 valve designs, the same principle), 4 cylinders is a total of 16 valves, we often see on the car data "16V" on the engine a total of 16 valves. This multi-valve structure is easy to form a compact combustion chamber, the injector arrangement in the center so that the oil and gas mixture can be more rapid and uniform combustion, the weight of the valve and the opening of the valve are properly reduced, so that the valve open or closed faster.
Composition of engine valve
A valve is composed of a valve head and rod. Valve head temperature is very high (intake valve 570 ~ 670K, exhaust valve 1050 ~ 1200K), and also under the pressure of the gas, valve spring force and transmission components inertia force, its lubrication, poor cooling conditions, requiring the valve must have a certain strength, stiffness, heat and wear resistance. Intake valves are generally alloy steel (chrome steel, nickel-chromium steel), and exhaust valves use the heat-resistant alloy (silicon chrome steel). Sometimes to save heat-resistant alloy, the exhaust valve heads with heat-resistant alloy, and the rod with chrome steel, and then the two are welded together.
The shape of the valve head is a flat top, spherical top and flared top, etc. Flat tops are generally used. Flat top valve head structure is simple, easy to manufacture, and a small heat absorption area, small mass, intake, and exhaust valves can be used. A spherical top valve is suitable for an exhaust valve, its strength is high, exhaust resistance is small, exhaust gas elimination effect is good, but its heat area is large, mass and inertia are large, and the processing is complicated. The flared type has a certain streamlined shape, which can reduce the intake resistance, but its head has a large heat area and is only suitable for intake valves.

The difference between engine valve and throttle
Valve and throttle are not the same things, their role and installation of the location are also different. The valve is divided into intake and exhaust valves, its role is to complete the internal combustion engine (including gasoline engines and diesel engines) four-stroke "intake. Compression. work. Exhaust" work cycle of important control components, it is installed in the engine cylinder body.
Throttle is often said (gasoline engine) "throttle", its role is to control the amount of mixed vapor into the cylinder, the driver when driving "gas" or "loose oil" In fact, it is changing the size of the throttle opening (changing the amount of mixture into the cylinder) to achieve the acceleration or deceleration of the car.
Warm Tips:
The gasoline engine has both valves and throttle, while the diesel engine has only valves and no throttle. The change of the gas pedal of the diesel car is to control the amount of fuel injected by the high-pressure oil pump to achieve the acceleration or deceleration of the car.